Sand casting, as the name suggests, is a casting process that uses a mold made from a special type of sand to form the desired part.
What is Casting Technology?
Casting is one of the oldest metal manufacturing techniques.
However, many of the objects we use in our daily lives are made using the Casting Process.
While its core technique remains essentially the same, it has evolved to become more precise and automated.
One of the innovations of the process is the ability to 3D print molds. We will return to this later in the article.
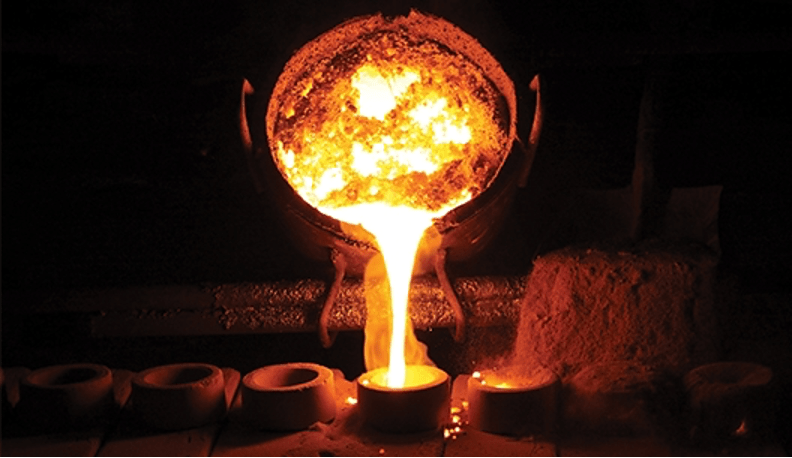

Molten metal is poured into a mold.
The process itself is quite simple. The liquid form of the metal material is poured into a mold that has the desired shape of the part. The metal will solidify into the shape of the mold. Once the metal has cooled, the part is ready to be removed, which is the final step in the process.
By definition, a casting is an object created by pouring liquefied material into a mold.
Types of casting processes
Over time, this process has evolved into different types of manufacturing methods. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages.
The most common types of casting processes today are:
- Sand casting
- Investment casting
- Pressure casting
- Plaster casting
What are the steps in the Casting Process?
The steps in the casting process are very similar for each type of technique available. Although there are variations in the steps involved, the basic operations are:
Making a Pattern
A pattern is a physical model that is used to make a mold and replicate the exterior of the casting. A number of materials can be used to create patterns. In many cases, the inside of a component needs to be hollow – such as a pipe fitting. This requires the creation of additional patterns called cores.
Making a Core
A core is a separate part of the mold that prevents liquefied material from filling that space. They are used to create internal cavities and other features that the mold cannot create. The tool used to make the core is called a core box, which is another name for a core mold. The materials used to create the core need to meet several requirements:
It must be strong enough to resist the turbulence caused by the molten material
Good hardness;
High permeability so that gases formed during the casting process can easily escape.
Resistant to high temperatures from the molten material.
Weak enough to break while the molten material cools and contracts, facilitating its removal after solidification.
Smooth surface finish.
Minimal gas generation when in contact with the molten material.
Molding
The process of creating the mold into which the molten metal will be poured. It involves several essential operations to form the mold around the pattern. The mold is contained in a thermowell, a frame consisting of two parts: the armature and the damper. The damper around the pattern is filled with molding sand, and then the pattern is removed.
The gating system, the channels that allow the molten material to flow into and through the mold, is positioned in the damper. It is also the resistance that receives the cores.
The hole through which the molten material is poured into the mold is placed in the canister.
Then, to close the mold, the mold is placed on top of the drawbar. Both parts are clamped together.
Melting and Pouring
Melting is the process of converting solid metal material into a liquid state so that it can be poured into the mold. The process is carried out at extremely high temperatures in a heating chamber called a furnace.
These chambers are designed based on many factors but mainly on the type of material and the fuel that will be used to reach the required temperature – which can be up to over 1600 ° C.
Exposing the metal to such extreme temperatures often produces toxic gases that can cause defects in the casting process. These gases are removed when the molten material is purified. This important step also purifies the metal material by extracting unwanted elements without changing its chemical structure. After refining, the molten material is ready to be tapped into a ladle. Ladles are used by foundries to safely transport and pour the molten metal into molds.
The metal is poured into the mold and allowed to cool until it reaches room temperature. Once the material solidifies, it undergoes a process called shaking out. The shaking out process separates and removes sand from the casting by vibrating the mold.
Cleaning
The casting is now ready and is removed from the mold. The gating system and any remaining material are removed. Excess material is trimmed. Post-treatment may be performed to improve the appearance and surface finish of the casting. And finally, the casting is inspected for quality control.
What is Sand Casting?
Sand casting is the most common technique for producing metal castings. According to Dr. TV Ramana Rao, Professor of Mechanical Engineering at Osmania University, India, who teaches Metal Casting and CAD/CAM, this technique accounts for over 70% of all castings produced.
The Sand Casting process is known for its versatility.
After all, it can produce castings of any size and weight with complex shapes using a large portion of the metal.
The main feature of the Sand Casting technique is that it uses sand as the casting material.
The significant cost reduction by using sand to make the molds instead of other materials is a big advantage. Especially when we consider that the cost of molding accounts for a large part of the cost of other casting techniques.
However, the nature of sand means that the molds used in this process cannot be reused. The sand mold cannot be retained when the casting is removed.
On the other hand, Sand Casting is ideal for metals with high melting points such as titanium, steel, and nickel. This is the only casting method that can handle these materials.
This technique is the first choice for small and economical mass production of parts in the aerospace and automotive industries.
If you are wondering how to use sand as a mold material, we will cover that topic right now
Sand mold material
Sand casting typically requires the following four components:
Base Sand
Base Sand is the sand used to make the mold in its pure state.
For it to hold together, a binding agent is needed.
Base Sand is also used to make the core.
The most common types of base sand are:
Silica Sand
Olivine Sand
Chromite Sand
Zircon Sand
Chamotte Sand
Binder
The most common types of binders are:
Clay and Water
Oil
Resin
Sodium Silicate
Additives
These are responsible for improving the mold in terms of surface finish, strength, cushioning, and heat resistance.
Release Compound
A liquid or fine powder used to release the sample from the mold.
Advantages of Sand Casting
The main advantages of Sand Casting are:
It can be used to produce parts from almost all metal materials, including those with high melting points;
Easily scalable;
Complex geometries with thin-walled sections;
Casting in any size and weight, and;
Low production costs.
Limitations of Sand Casting
The main limitations of Sand Casting are:
High volume production requires a high level of automation for the molding process;
Lower accuracy than other methods, and;
Rough surface finishes often require post-treatment.
Reinventing the Casting Process with 3D Printing
The ability to create 3D printed molds for sand casting is a game changer.
Combining additive manufacturing with mold making methods is reinventing the casting process and addressing some of its limitations.
This hybrid model offers a competitive advantage over traditional manufacturing processes due to its economic and design benefits.
OTHER NEWS